Real-World Examples of Art Therapy Supporting PTSD Emotional Recovery
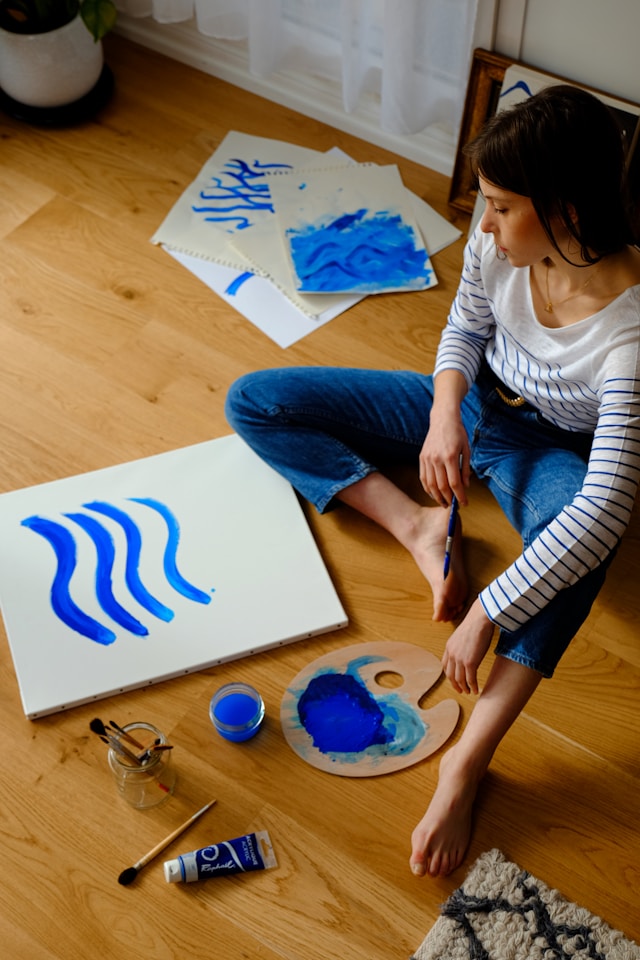

The Transformative Power of Art Therapy in PTSD Treatment
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex mental health condition that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Traditional therapeutic approaches such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and medication are often employed to treat PTSD, yet they may not work for everyone. Art therapy has emerged as a powerful alternative, offering a unique avenue for individuals to process trauma and regain emotional stability. By engaging in creative expression, individuals can explore difficult emotions in a non-verbal manner, which can be particularly beneficial for those who find talking about their experiences challenging.
Case Study 1: Painting as a Path to Healing
Consider the case of John, a veteran who struggled with severe PTSD after serving in combat zones. John participated in an art therapy program where painting was used as a medium to express his inner turmoil. Initially reluctant, John gradually found that painting allowed him to externalize his experiences and feelings without having to articulate them verbally. Over time, his paintings evolved from chaotic and dark imagery to more structured and colorful compositions, reflecting a shift in his mental state.
Benefits:
- Non-verbal Expression: Art therapy provided John a safe space to express emotions he could not put into words.
- Sense of Control: Through creating art, John regained a sense of control over his experiences, which is crucial in PTSD recovery.
Challenges:
- Initial Resistance: John’s initial skepticism highlighted the need for therapists to build trust and encourage openness towards creative methods.
This example demonstrates the potential for art therapy to facilitate emotional healing when traditional talk therapies fall short.
Case Study 2: Collage and Emotional Integration
Alice, a survivor of domestic violence, turned to art therapy as a means to cope with her PTSD symptoms. In her sessions, she utilized collage-making to piece together fragmented memories and emotions. The process of selecting images and arranging them allowed Alice to construct new narratives and meaning from her traumatic experiences. This visual storytelling served as a bridge between her conscious thoughts and subconscious emotions.
Pros:
- Symbolic Representation: Collage-making enabled Alice to represent complex emotions through symbols, easing the integration of traumatic memories.
- Empowerment: Creating collages gave Alice agency over her past, transforming her role from victim to creator.
Cons:
- Emotional Overwhelm: At times, Alice felt overwhelmed by the memories that surfaced during the creative process. It required careful guidance from her therapist to navigate these emotions safely.
The Role of Art Therapists
Art therapists play a crucial role in facilitating these healing processes. They provide a supportive environment where individuals feel safe to explore their emotions. Trained to interpret the imagery clients create, art therapists can guide discussions that help individuals make sense of their artwork and connect it to their personal experiences.
An effective art therapist tailors the approach based on each client’s needs, preferences, and progress. This personalized touch is essential for ensuring that art therapy is both meaningful and effective.
Practical Tips for Implementing Art Therapy
- Create a Safe Space: Ensure the environment is comfortable and private, allowing individuals to express themselves without judgment.
- Encourage Open-Ended Creation: Let participants know there is no right or wrong way to create art; the focus is on expression rather than technical skill.
- Focus on Process over Product: Emphasize the therapeutic journey of creating rather than the finished artwork.
When to Consider Art Therapy for PTSD
Art therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals who:
- Struggle with verbal communication or have difficulty articulating their trauma through words.
- Have not found relief through traditional therapies alone.
- Are open to exploring new forms of self-expression.
For healthcare professionals considering incorporating art therapy into treatment plans, it is important to collaborate with trained art therapists who understand the complexities of PTSD and can guide the creative process appropriately.
The Future of Art Therapy in Mental Health
The recognition of art therapy's potential continues to grow within the field of mental health. As research expands and more case studies illustrate its efficacy, art therapy may become more widely integrated into treatment protocols for PTSD and other mental health conditions.
In conclusion, art therapy offers a powerful, non-verbal method for individuals with PTSD to process trauma and foster emotional recovery. Through real-world examples like those of John and Alice, we see how creative expression can transform lives by helping individuals navigate their emotional landscapes in profound ways. As the mental health community embraces diverse approaches like art therapy, there is hope for more inclusive and effective treatment pathways for those suffering from trauma-related disorders.